Why Vitamin D-Rich Foods Are Important?
Index
| 1. Introduction |
| 2. The Role of Vitamin D in the Body |
| 3. Natural Sources of Vitamin D |
| 4. 5 Fruits High in Vitamin D |
| 5. 4 Vegetables Rich in Vitamin D |
| 6. Other Food Sources of Vitamin D |
| 7. Combining Vitamin D Sources |
| 8. Dietary Guidelines for Meeting Vitamin D Needs |
| 9. Cooking and Preparation Tips |
| 10. Supplements and Vitamin D Deficiency |
| 11. Conclusion |
| 12. Scientific Information About Vitamin D And Its Food Sources |
| 13. FAQs |
Vitamin D is one of the most vital vitamins for the human body. It plays a crucial role in building and maintaining bone health, supporting heart health, boosting the immune system, and contributing to better mental health. Vitamin D foods are readily available in various forms, making it easily obtainable through a balanced diet. While supplementation is convenient, it is essential to remember that Vitamin D naturally occurs in foods and should be an individual’s primary source of this essential nutrient.
The Role of Vitamin D in the Body
Vitamin D’s role in the body is widely discussed as it provides a range of benefits. Its importance in the body includes:
- The vitamin plays a vital role in calcium absorption from the intestines, which is essential for building and keeping bones strong and healthy.

- Known to boost the immune system, Vitamin D helps in the production of antimicrobial peptides and enhances the body’s defence against infections.
- Some studies suggest a connection between Vitamin D deficiency and conditions like depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD), especially considering that mental health issues like SAD tend to occur during the months when there is limited sunlight in the winter.
- Heart health is often regulated by Vitamin D as it helps prevent inflammation and maintain normal blood pressure.
- Vitamin D helps in improving muscle function and increases overall mobility and physical performance of the body because of its link to energy levels.

Natural Sources of Vitamin D
The sun is the most well-known source of Vitamin D. The body’s skin can synthesise Vitamin D when exposed to UVB rays. The UVB rays from the sun interact with a precursor compound in an individual’s skin, converting it into a form of vitamin D. Hence getting adequate amounts of sunlight is the best way of receiving some Vitamin D in one’s body. It is important to know that the time, location and intensity of sunlight determine how much Vitamin D an individual will be getting.
Vitamin D can be obtained through various dietary sources and supplements. Vitamin D foods that naturally contain Vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and trout), cod liver oil, small amounts of beef liver, egg yolks, and cheese. Along with this, fortification of Vitamin D in foods such as milk, cereals and orange juice may also serve as a source of the vitamin.
5 Fruits High in Vitamin D
Fruits are not considered a primary Vitamin D source, but certain types of mushrooms are considered to be high in Vitamin D and are a popular source of the vitamin in colder countries where sunlight is limited.
1. Maitake Mushrooms:
While not a fruit, maitake mushrooms can be considered a source of vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
2. Oranges:
Considered to be a good source of Vitamin D, oranges can be easily incorporated into one’s diet.
3. Sun-Dried Shiitake Mushrooms:
Shiitake mushrooms, when dried in the sun, can accumulate vitamin D2.
4. Bananas:
These fruits are considered to have amounts of Vitamin D along with magnesium.
5. Dried Figs:
Dried figs contain small amounts of vitamin D, although it is present in very modest quantities.
4 Vegetables Rich in Vitamin D
While vegetables are not considered to be Vitamin D rich foods, a few of them which are considered Vitamin D rich can be easily incorporated into one’s diet.
1. Spinach:
These leafy greens are considered to be a good vegetarian source of Vitamin D.
2. Kale:
Kale is considered an easy way to add Vitamin D to one’s diet because of its versatility in various dishes.
3. Okra:
Also known as ladyfinger in local languages, this vegetable is a good source of Vitamin D and can be consumed in a variety of preparation forms.
4. White beans:
White beans contain a decent amount of Vitamin D and can be consumed via soups, curries and much more.
Other Food Sources of Vitamin D
Other Vitamin D foods which do not fall under fruits and vegetables include:
- Meat (such as beef liver and chicken liver)
- Dairy (such as milk, cheese and eggs)
- Legumes ( such as beans, lentils and chickpeas)
- Grains (such as whole wheat pasta, oats and quinoa
- Seafood (such as salmon, trout and tuna)
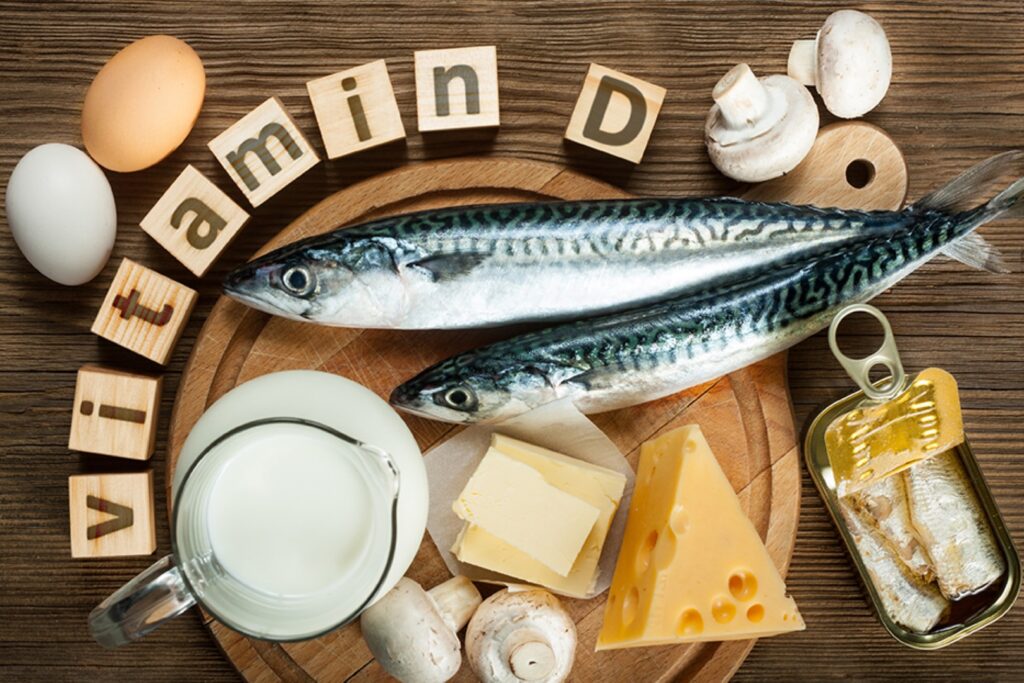

Combining Vitamin D Sources
Before one plans their meals and incorporates Vitamin D into them it’s important to understand the best sources of Vitamin D especially the natural sources of the vitamin. The primary food sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), fortified foods (cereals, milk, orange juice), egg yolks, and mushrooms (when exposed to sunlight).
Pairing food strategically can help combine Vitamin D rich foods with other nutritious ingredients to create well-balanced meals. For example:
- A salmon salad with leafy greens, cherry tomatoes, and a citrus vinaigrette.
- Make an omelette with spinach, tomatoes, and mushrooms.
- Create a yogurt dessert with fortified yogurt, berries, and granola.
Using fortified foods and additional supplementation is also one of the most efficient ways to add Vitamin D into one’s daily routine/diet.
Dietary Guidelines for Meeting Vitamin D Needs
How much Vitamin D an individual needs can vary depending on factors such as how much time they spend in the sun, their skin colour, where they live, what they eat, and the existing health conditions they have. Hence it is always recommended to speak to a healthcare professional before incorporating Vitamin D either through supplementation or not in one’s journey to better health.
Infants, children, adults and senior individuals would require different levels of Vitamin D to keep themselves healthy.
Cooking and Preparation Tips
Cooking meals that are Vitamin D-rich does not have to be boring. It can be tasty meals that make sure you get the adequate amount of Vitamin D needed for your body.
Certain methods of cooking and preparation are also said to enhance the retention of Vitamin D in the meal. These methods include:
- Vitamin D rich foods that are grilled or baked. Fish can be prepared easily this way.
- Fortified foods include cereals, orange juice and yogurt.
- Boiled eggs and sunny side up eggs are one of the best preparations for retaining egg nutrition.
- Sun-dried mushrooms obtain Vitamin D because of the absorption of Vitamin D while being sun dried.
- UV-exposed food may help with the addition of mild Vitamin D in them.
Supplements and Vitamin D Deficiency
The symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency include fatigue, weak immune systems, low energy levels, bone/muscle pain and mental health issues (such as depression and mood disorders).
In the long run, these issues can turn chronic and cause diseases like osteoporosis, rickets (in children), autoimmune disorders and arthritis.
Supplements are a great way to get the Vitamin D individuals require to treat deficiencies or maintain a balanced diet. Certain individuals such as those with darker skin tones, who are older and have limited sun exposure may reap the benefits of taking Vitamin D supplementation.

Vitamin D tablets are available in two main forms: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Conclusion
Vitamin D provides a wide range of benefits to the human body, such as the maintenance of bones and muscles, improved immune system function, better mood and mental health, and heart health support.

While sunlight is considered the best source of vitamin D, various vegetables, fruits, cereals, and meats provide a good amount of Vitamin D that can be incorporated into one’s daily meals. These are essentially natural Vitamin D sources.
Scientific Information About Vitamin D And Its Food Sources
-The Influence of Storage and Cooking on the Vitamin D Content
-Effects of Different Cooking Methods on the Vitamin D
-Revisiting Food-sourced Vitamins for Consumer Diethttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8418216/
FAQs
Are fortified foods a reliable source of Vitamin D?
Yes, they are a reliable source of Vitamin D.
Is there a difference in Vitamin D content between fresh and canned fruits and vegetables?
Yes, there may be a difference between the two.
What is the importance of Vitamin D in our diet?
Vitamin D aids bone health, heart health, mental health and improves immunity.
Can vitamin D-rich foods be beneficial for individuals with skin conditions that limit sun exposure?
Yes, they can be beneficial for individuals with skin conditions that limit sun exposure.